Joint Clinic I will always provide care with sincerity and dedication.
Common Causes of Knee Pain: Ligament Tears, Meniscus Damage, and Osteoarthritis

Ligament Tears
When the knee is subjected to strong impact during daily activities or exercise, the ligaments can tear or become damaged. In particular, the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) are common causes of knee pain. However, in cases of mild damage, the symptoms may be subtle, leading to neglect. If a cruciate ligament injury is left untreated, the cartilage inside the knee can also be damaged, potentially resulting in bone friction and worsening into osteoarthritis.Meniscus Damage
The meniscus is a crescent-shaped piece of cartilage located on the inner and outer sides of the knee joint. It helps reduce friction between bones, absorbs shock, and alleviates pressure in the knee. If meniscus damage is left untreated, the torn cartilage can gradually worsen, leading to osteoarthritis over time.

Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis occurs when the cartilage that protects the knee joint deteriorates due to aging or joint injury. As the cartilage degenerates, the bones start to come into direct contact with each other, causing damage to the bones, ligaments, and other structures, leading to inflammation and pain. If osteoarthritis is not treated early and is left untreated, it can result in severe pain and joint deformities.Causes of Osteoarthritis

Primary Osteoarthritis
This form of arthritis occurs without any
Secondary Osteoarthritis
This type of osteoarthritis develops after conditionsSymptoms of Osteoarthritis
Pain caused by osteoarthritis is typically worse in the afternoon than in the morning.
As the condition progresses to its later stages, swelling and fluid accumulation in the knee can occur, leading to
persistent pain throughout the day. The main symptoms of osteoarthritis include:

Osteoarthritis Diagnosis
Osteoarthritis can be relatively easily diagnosed using X-rays. However, in elderly patients, some degree of degenerative changes are a natural occurrence, so diagnosis should be made by combining medical history and physical examinations. Additionally, depending on the severity and duration of symptoms, ultrasound, MRI, and blood tests may be required.
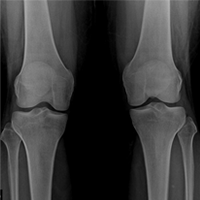 Normal X-ray
Normal X-ray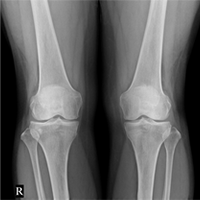 Early-stage Osteoarthritis
Early-stage Osteoarthritis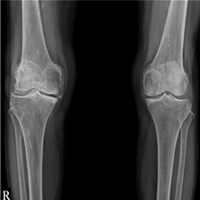 Advanced-stage Osteoarthritis
Advanced-stage OsteoarthritisOsteoarthritis Treatment and Prevention
| Conservative Treatment | Exercise Therapy | Improving lifestyle and preventing muscle weakening |
| Medication Therapy | Treatment to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain in the joints | |
| Injection Therapy | a. Cartilage Injections, DNA Injections: Regenerative treatment for knee joint cartilage b. Ligament Strengthening Injections: Treatment to strengthen the muscles and ligaments supporting the knee |
|
| Surgical Treatment | If conservative treatments are no longer effective or joint deformities continue to progress, causing significant disruption to daily life, surgical treatments such as arthroscopic surgery or knee joint replacement surgery may be required. | |
| Prevention | Posture | Avoid postures that strain the knee joint, such as squatting, in daily life. |
| Weight Management | It is known that if body weight increases by 1 kg, the pressure on the knee joint can increase by 3 to 20 times. Therefore, it is advisable to maintain an appropriate weight. | |
| Exercise | It is beneficial to continue exercises that strengthen the surrounding tissues of the knee and the thigh muscles. | |