Joint Clinic I will always provide care with sincerity and dedication.

Shoulder pain is commonly experienced during everyday activities, such as reaching for something on a shelf, twisting the arm behind to put on clothes, or turning the hand to fasten a seatbelt. When shoulder pain occurs, many people self-diagnose it as "frozen shoulder" (adhesive capsulitis). However, shoulder pain can have various causes, not just "frozen shoulder." Other possible causes include rotator cuff disorders, calcific tendinitis, impingement syndrome, and even cervical disc herniation. Because shoulder pain can result from many different conditions, it is important to get an accurate diagnosis and receive appropriate treatment tailored to the specific cause.
Frozen
Shoulder

Rotator Cuff
Disorder

Shoulder Impingement
Syndrome

Calcific
Tendonitis

Cervical Disc
Herniation

What is Frozen Shoulder?
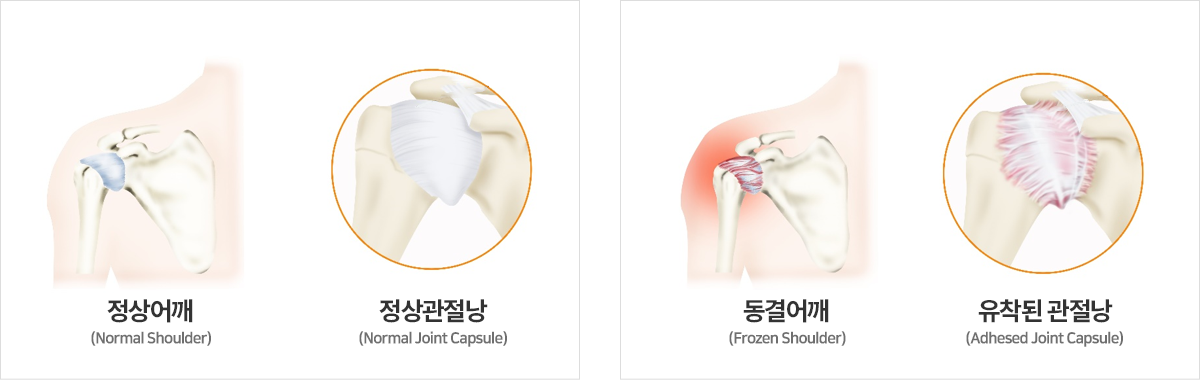
Frozen shoulder, or adhesive capsulitis, is a condition in which degenerative changes in the joint capsule surrounding the shoulder cause inflammation.This leads to the formation of adhesions within the shoulder joint, resulting in pain and restricted range of motion when the arm is moved.Although the term "frozen shoulder" originated because it is commonly seen in individuals in their 50s, it is increasingly affecting younger age groups, with the terms "frozen shoulder" in the 40s and even 30s becoming more common. In fact, it is also seen in adolescents and young adults who have insufficient physical activity, such as those who spend long hours sitting at desks. The condition is often referred to as "frozen shoulder" due to the sensation of the shoulder "freezing" and becoming immobile. The medical term for this condition is "adhesive capsulitis," which refers to the thickening and tightening of the joint capsule, leading to the restriction of movement and pain.
Causes of Frozen Shoulder
Frozen Shoulder Symptoms

As frozen shoulder progresses, the pain becomes so severe that it can limit the range of motion to the point where normal daily activities become impossible. Initially, the movement of the arm when rotating it backward becomes restricted, followed by difficulty lifting the arm sideways, and eventually, the forward motion is also restricted. A characteristic feature of frozen shoulder is that the pain worsens at night. Unlike conditions like arthritis or neuralgia, where pain typically occurs during or after movement, frozen shoulder pain intensifies when lying still at night.
Frozen Shoulder Diagnosis
 Patient history and
Patient history and
 Ultrasound and
Ultrasound andFrozen Shoulder Treatment
 Injection therapy &
Injection therapy &  Exercise therapy
Exercise therapy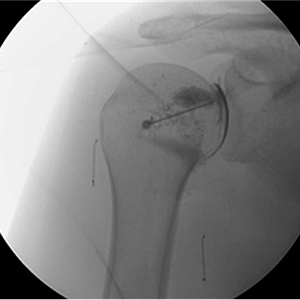 Adhesiolysis
AdhesiolysisPain Prevention Stretching

What is Rotator Cuff Disease?
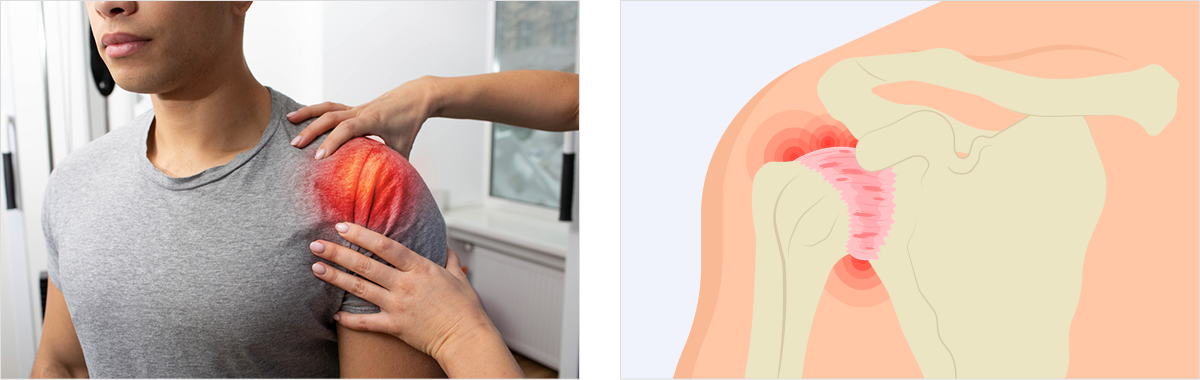
The rotator cuff refers to a group of tendons in the shoulder that play a key role in lifting and rotating the arm. As we age or with frequent use of the shoulder, repetitive stress or impact can lead to inflammation in the rotator cuff, resulting in pain. This condition is collectively referred to as rotator cuff disease. As the disease progresses, bone spurs may form, and the tendons may become inflamed, causing pain and weakness when lifting the shoulder. This stage is known as impingement syndrome. If left untreated, it can lead to a tear in the tendons, called rotator cuff tear.
Causes of Rotator Cuff Injury
Symptoms of Rotator Cuff Injury

Symptoms of Rotator Cuff Injury
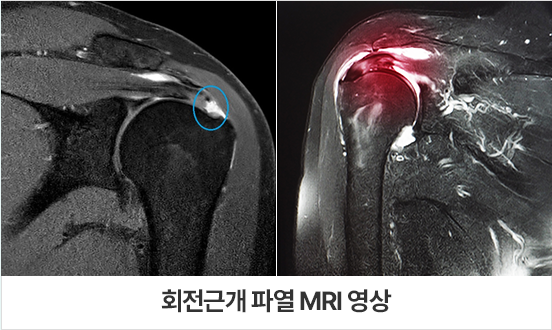
Rotator cuff tears can often be diagnosed through a detailed medical history and physical examination. For example, if the patient can raise the painful arm with the help of the opposite arm, a rotator cuff tear is suspected. If the arm cannot be raised, frozen shoulder is more likely. Some patients may be told that there is no issue with the shoulder after an X-ray at a non-specialized clinic. However, if a rotator cuff tear is left untreated, it can lead to frozen shoulder. Distinguishing between the two conditions can be challenging, so accurate diagnosis is essential. A rotator cuff tear can only be confirmed through ultrasound or MRI.
Treatment for Rotator Cuff Disorders
 Injection Therapy & Medication
Injection Therapy & Medication Exercise Therapy
Exercise Therapy Surgical Treatmen
Surgical TreatmenPain Prevention Stretches

What is Calcific Tendonitis?
Calcific tendonitis is a condition commonly seen in individuals in their 40s, where calcium deposits form in the tendons of the shoulder. The exact cause is unclear, but it is believed that tendon cells transform into cartilage cells, leading to the formation of calcium deposits. These deposits cause severe pain when they form and later get absorbed.
Symptoms of Calcific Tendonitis

Diagnosis of Calcific Tendonitis
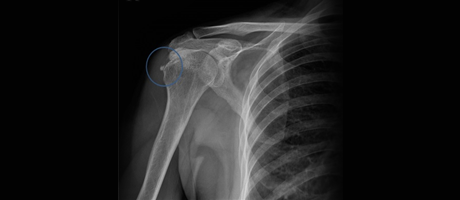
Calcific Tendonitis X-ray
Calcific tendonitis can be diagnosed through X-ray imaging,
which reveals the calcifications formed in the tendon.
Pain Prevention Stretches
